Introduction
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is a directional momentum indicator that depicts the connection between two EMAs, most often the 12-period (fast) and 26-period (slow). It assists traders in determining trend direction, changes in momentum, and potential buy/sell signals. Technical analysis is an essential component of modern trading methods, allowing traders to make sound judgments based on historical market data, price activity, and statistical indicators. Among the thousands of indicators available, only a handful have stood the test of time: the relative strength index (RSI), the moving average convergence divergence (MACD), and the moving average. These tools assist traders in determining market momentum, trend direction, and possible reversal points. This book teaches you how to utilize RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages successfully, as well as how to combine them with modern trading tools for more advanced analysis.
Understanding RSI (relative strength index)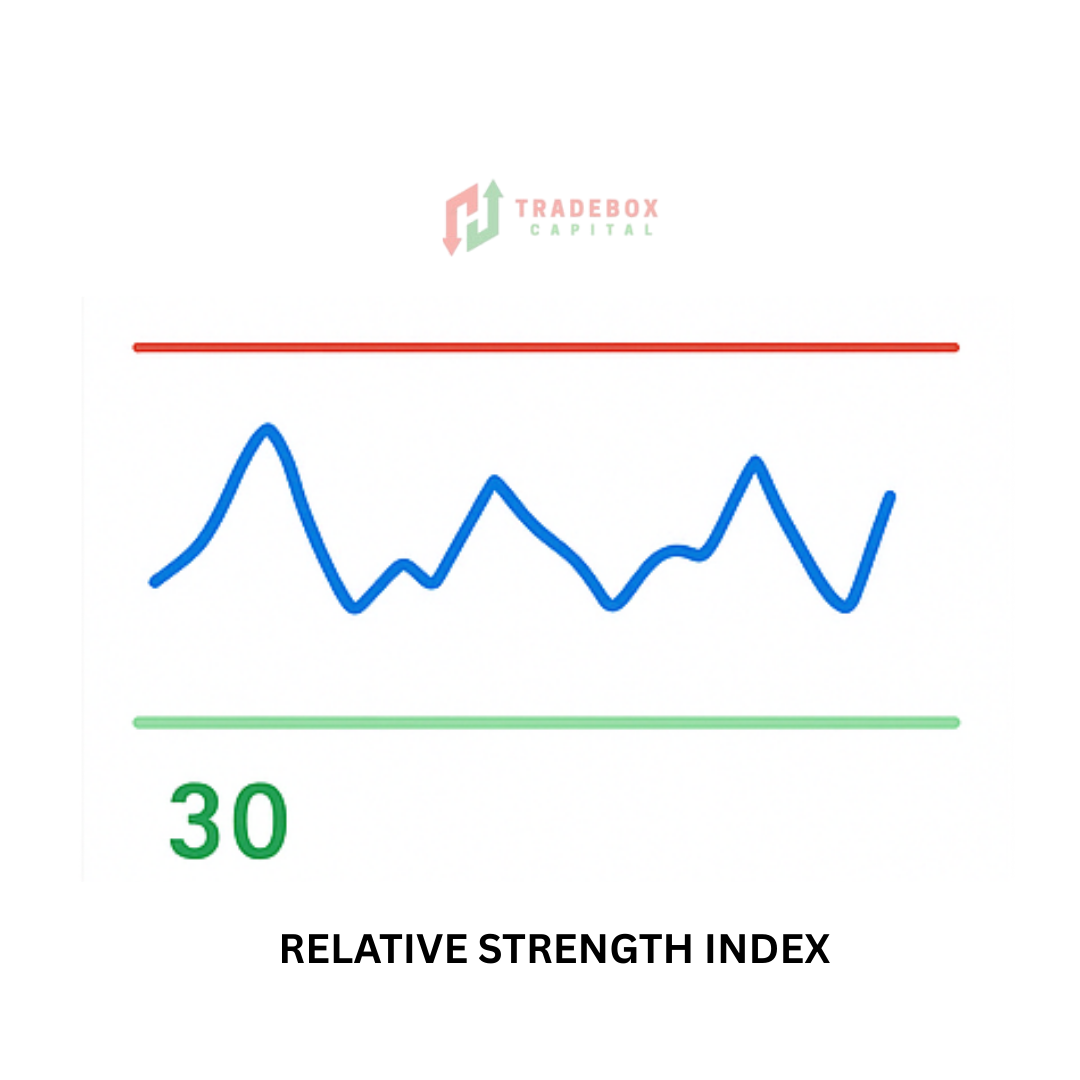
The (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that monitors the rate and magnitude of price fluctuations. It spans from 0 to 100 and is widely used to indicate overbought or oversold market conditions. RSI helps traders predict price reversals and identify probable entry and exit locations.
Key Levels of RSI (relative strength index)
Above 70: An overbought condition, indicating a likely downward correction.
– Below 30: An oversold state, indicating a possible upward correction.
– 50: The midline is typically used to determine trend direction (above 50 indicates bullish momentum, below 50 shows negative momentum).
How to Use RSI in Trading
- Overbought and Oversold Strategy
Traders often buy when RSI breaks above the 30 level after being oversold and sell when it falls below 70 after being overbought.
- RSI Divergence
Divergence occurs when the price makes a new high or low, but RSI fails to do so. This signals a weakening trend and a likely reversal.
- Trend Confirmation
RSI can confirm trends when it consistently stays above 50 during uptrends and below 50 during downtrends.
Using Tools with RSI
Modern trading tools allow traders to:
- Set RSI alerts on trading platforms.
- Backtest RSI-based strategies.
- Combine RSI with automated bots for signal-based trades.
- Visualize RSI divergences automatically.
Understanding MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
MACD is a momentum indicator that follows trends and displays the relationship between two price moving averages. It is made up of the MACD Line, Signal Line, and Histogram. MACD enables traders to understand momentum shifts, trend strength, and probable trend reversals.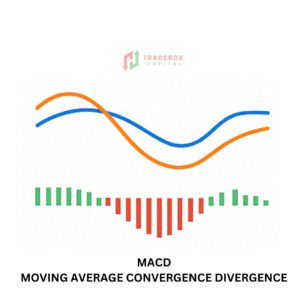
Components of MACD
MACD Line: Difference between the 12-period and 26-period EMA.
- Signal Line: 9-period EMA of the MACD Line.
- Histogram: Represents the distance between the MACD and Signal Line.
How to Use MACD in Trading
- MACD Line and Signal Line Crossovers
When the MACD crosses above the Signal Line, it generates a bullish signal. When it crosses below, it’s bearish. - Zero Line Crossovers
A bullish trend is confirmed when MACD crosses above the zero line; a bearish trend is confirmed when it moves below. - MACD Divergence
Divergence between MACD and price action often precedes reversals.
Using Tools with MACD
Trading platforms provide tools that:
- Highlight MACD crossovers.
- Visualize histogram momentum shifts.
- Offer automated alerts for MACD-based signals.
- Allow traders to customize MACD settings for different markets.
Understanding Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data, making it easier to see trends. They are some of the most basic and effective indicators in technical analysis. Simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA) are two common types.
Types of Moving Averages
- Simple Moving Average (SMA)
Average of closing prices over a specific period. - Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
Gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new trends.
Popular Moving Average Periods
- 20-day: Short-term trend.
- 50-day: Medium-term trend.
- 200-day: Long-term trend.
How to Use Moving Averages in Trading
- Trend Identification
If price stays above a moving average, the trend is bullish; if below, bearish. - Moving Average Crossovers
Example: A golden cross occurs when the 50-day MA crosses above the 200-day MA. -
Dynamic Support and Resistance
Moving averages act as support in uptrends and resistance in downtrends.
Using Tools with Moving Averages
Tools help traders by:
- Plotting multiple MAs simultaneously.
- Generating alerts when price crosses an MA.
- Back testing MA crossover strategies.
- Using algorithmic trading bots to execute MA-based trades.
Combining RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages
Combining these indicators creates a comprehensive trading strategy. Each indicator provides different insights:
- RSI: Overbought/oversold and momentum shifts.
- MACD: Trend direction and strength.
- Moving Averages: Trend structure and key price levels
Strategies for Combining Indicators
Trend Confirmation Strategy
- Use moving averages to identify the trend.
- Use MACD to confirm trend momentum.
- Use RSI to time entries and exits.
Reversal Strategy
- RSI divergence signals a potential reversal.
- MACD crossover confirms momentum shift.
- Price breaking a key moving average confirms trend reversal.
Momentum Strategy
- RSI rising from oversold indicates strong buying interest.
- MACD histogram turning positive shows increasing momentum.
- Price bouncing from a moving average confirms the upward move.
Using Tools to Combine Indicators
Modern trading platforms offer:
- multi-indicator dashboards.
- Trading bots that use RSI, MACD, and MA rules.
- Back testing engines for strategy optimization.
- Alerts for combined indicator conditions.
Advanced Techniques with RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages
Risk Management Tools
Indicators help traders set:
- Stop-loss levels based on MA support.
- Take-profit targets based on RSI overbought zones.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Relying on a single indicator.
- Overtrading based on minor signals.
- Ignoring risk management.
Not back testing strategies before live trading
Conclusion
RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages remain essential tools for technical traders. By understanding how each indicator works and learning to combine them effectively, traders can improve their accuracy, reduce emotional trading, and develop strong, rule-based strategies. With the help of modern trading tools—such as alerts, back testing platforms, and automated bots—these indicators become even more powerful. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced trader, mastering these three indicators will significantly enhance your trading skill and confidence.
What is the main purpose of using RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages in trading?
These indicators assist traders in determining market momentum, recognizing trend direction, and identifying potential reversal signs. When used together, they provide a fuller picture of market conditions, resulting in better overall trading decisions.
How does RSI help traders decide when to buy or sell?
When the RSI exceeds 70, it indicates overbought situations, and when it falls below 30, it shows oversold conditions. Traders frequently purchase when the RSI rises over 30 (indicating a recovery in momentum) and sell when it falls below 70. RSI divergence is sometimes used to anticipate future reversals.
What do MACD crossovers mean in trading?
A bullish signal occurs when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, while a bearish signal occurs when it crosses below. Crossovers can assist traders in identifying momentum shifts and confirming trend strength, especially when the MACD swings above or below zero.
Why are moving averages important for identifying trends?
Moving averages level out price data, making trends simpler to spot. If the price remains above the MA, the trend is normally bullish; if it falls below, it is bearish. Crossovers (such as the 50-day moving above the 200-day) can also assist traders predict major trend shifts.
How can modern trading tools enhance the use of RSI, MACD, and Moving Averages?
Modern platforms enable notifications, automated signals, back testing engines, and bot integration. These tools enable traders to spot indicator patterns, test strategies, and execute trades more precisely and with less emotional distraction.